Financial Models
How to Build a Bar/Pub Financial Model: Key Considerations and Tips
Creating a successful financial model for a bar or pub is essential for new and seasoned entrepreneurs. A well-crafted financial model helps in forecasting revenue and expenses, securing funding, and managing operations efficiently. In this article, we’ll guide you through the key steps and considerations in building a robust bar/pub financial model using Excel financial model templates.
1. Understand the Purpose of Your Financial Model
Before diving into the specifics, it’s important to understand why you need a financial model for your bar or pub. Here are some primary purposes:
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Predict future revenues, costs, and profits.
- Investment Analysis: Attract investors by showcasing potential returns.
- Operational Planning: Aid in strategic decision-making and day-to-day management.
- Performance Monitoring: Track actual performance against projections and adjust strategies accordingly.
2. Gather Essential Data
Accurate data is the backbone of any financial model. Gather the following information:
- Historical Financial Data: Past income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Market Research: Industry trends, competitor analysis, and market demand.
- Operational Data: Information on drink and food prices, peak hours, and customer demographics.
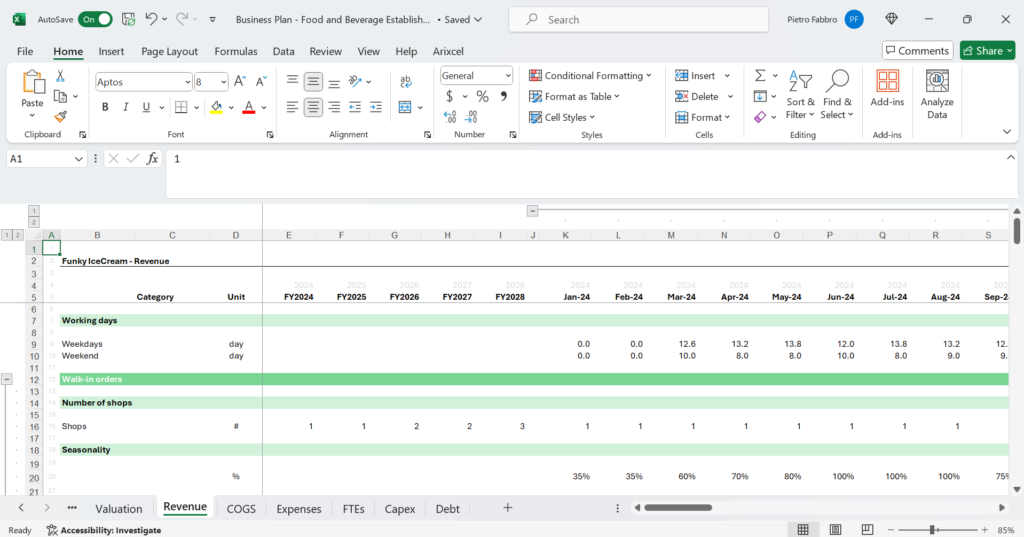
3. Revenue Projections
Revenue projections are the cornerstone of your financial model. Consider the following:
- Sales Mix: Estimate the percentage of revenue from different categories such as drinks, food, and special events.
- Average Transaction Value: Calculate the average spend per customer.
- Customer Footfall: Estimate the number of customers per day, week, or month.
- Seasonal Variations: Account for fluctuations in demand based on seasons, holidays, and local events.
- Special Events: Include projections for special events like live music, trivia nights, and private parties.
4. Cost Assumptions
Identifying and categorizing costs is crucial. Divide them into three main categories:
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
These are direct costs associated with serving drinks and food.
- Beverage Costs: Costs of alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages.
- Food Costs: Costs of ingredients for menu items.
- Bar Supplies: Costs for items like napkins, straws, and glassware.
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses are the day-to-day costs incurred to run your bar or pub.
- Fixed Costs:
- Rent or Mortgage: Monthly payments for the property.
- Insurance: Property and liability insurance premiums.
- Utilities: Water, electricity, gas, and internet services.
- Licenses and Permits: Costs for liquor licenses and other necessary permits.
- Variable Costs:
- Staff Wages: Salaries for bartenders, servers, cooks, and cleaning staff.
- Marketing and Advertising: Costs associated with promoting your bar or pub (online ads, print ads, etc.).
- Maintenance and Repairs: Costs for regular upkeep and unexpected repairs.
- Entertainment: Costs for live music, DJs, or other entertainment.
Capital Expenditures (Capex)
Capex includes long-term investments in the property.
- Furniture and Fixtures: Costs for furnishing the bar with tables, chairs, bar stools, etc.
- Renovations: Costs associated with refurbishing or upgrading the property.
- Kitchen Equipment: Purchase of kitchen appliances, refrigeration units, and other major equipment.
- Bar Equipment: Purchase of items like taps, mixers, and coolers.
- Technology: Point of sale systems, sound systems, and security cameras.
5. Break-Even Analysis
Conducting a break-even analysis helps determine the minimum revenue required to cover costs. Calculate:
- Fixed Costs: Sum of all fixed expenses.
- Contribution Margin: Average revenue per customer minus variable cost per customer.
- Break-Even Point: Fixed Costs ÷ Contribution Margin.
6. Cash Flow Projections
Cash flow is the lifeblood of your bar or pub. Ensure you have a detailed cash flow statement to:
- Track Inflows and Outflows: Monitor all sources of cash (sales revenue, event fees) and uses of cash (expenses, loan repayments, capital expenditures).
- Manage Working Capital: Keep an eye on accounts receivable and payable.
7. Sensitivity Analysis
A sensitivity analysis assesses how changes in key assumptions affect your financial projections. This helps in:
- Risk Management: Identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies.
- Decision Making: Evaluate the impact of different scenarios (e.g., changes in customer footfall, pricing adjustments).
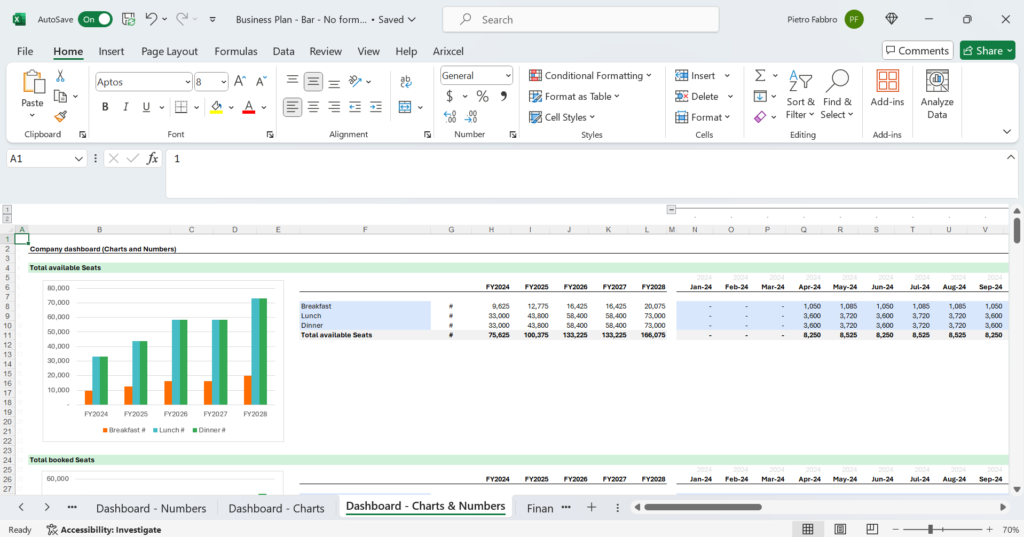
8. Regular Updates and Monitoring
A financial model is not a one-time exercise. Regular updates and monitoring are essential for accuracy and relevance:
- Periodic Reviews: Compare actual performance with projections and adjust assumptions as needed.
- Scenario Planning: Continuously assess the impact of new variables and market trends.
9. Use Financial Model Templates
Building a financial model from scratch can be daunting. Using a professionally designed Excel financial model template can save time and ensure accuracy. Templates typically include:
- Pre-Built Formulas: Eliminate the risk of calculation errors.
- Comprehensive Layouts: Cover all necessary components like income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Customizable Features: Tailor the template to suit your specific needs.
Conclusion
Creating a robust bar/pub financial model is critical for success in the competitive hospitality market. By following the steps outlined above and considering all relevant factors, you can build a financial model that provides valuable insights and supports strategic decision-making. For an even easier and more accurate approach, consider investing in a professional Excel financial model template. Our Excel financial model templates are designed to help you build comprehensive, reliable financial models with ease.
By focusing on these key elements, you’ll be well on your way to creating a financial model that can help your bar or pub business thrive. Don’t forget to check out our wide range of Excel financial model templates designed specifically for the hospitality industry. Start building your financial success today!


